Asset Allocation
Asset Allocation is the process of dividing an investment portfolio among different asset categories, such as stocks, bonds, commodities, and cash. The goal is to balance risk and reward by apportioning the portfolio’s assets according to an individual’s goals, risk tolerance, and investment horizon.
The enemy of a good asset allocation is the quest for a perfect one. Fight the urge to be perfect.
- Richard A. Ferri
How to Calculate Asset Allocation?
Calculating asset allocation involves determining the percentage of the total portfolio invested in each asset class. Here’s a simplified method:
List all assets
Identify all the assets in your portfolio:
| Category | Allocation |
|---|---|
A | $60,000 |
B | $30,000 |
C | $10,000 |
Determine the total value
Calculate the total value of the portfolio by summing the values of all assets.
Total Value: $60,000 + $30,000 + $10,000 = $100,000
Calculate the percentage
Divide the value of each asset class by the total portfolio value and multiply by 100 to get the percentage.
| Category | Calculation | Allocation | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
A | ($60,000 / $100,000) * 100 | $60,000 | 60% |
B | ($30,000 / $100,000) * 100 | $30,000 | 30% |
C | ($10,000 / $100,000) * 100 | $10,000 | 10% |
Tip: Diversify your portfolio across uncorrelated assets to minimize risk while maintaining growth potential. Think stocks, bonds, and commodities.
The Importance of Asset Allocation in Trading
Asset allocation is a important process that involves dividing a portfolio across various asset classes like stocks, bonds, and cash to balance risk and reward. It ensures diversification, reducing the impact of poor performance in any single asset class. Proper allocation aligns investments with an individual’s financial goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon, providing a structured approach to wealth building. By adapting to changing market conditions, asset allocation enhances the potential for long-term stability and growth.
Caution: Avoid overallocating to highly volatile assets. A balanced approach helps protect against drastic portfolio swings.
Asset Allocation in Practice
This section demonstrates how different asset allocation strategies: balanced, aggressive, and conservative can be applied in real-world scenarios. These examples provide insights into tailoring your portfolio to align with specific goals, such as maximizing growth, balancing risk, or preserving capital. By exploring these scenarios, you’ll gain a practical understanding of how asset allocation impacts portfolio performance and risk management.
Balanced Asset Allocation
A balanced asset allocation strategy typically involves dividing investments equally among various asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and commodities. Let’s consider an example where a trader allocates their $100,000 portfolio as follows:
| Asset Class | Allocation | Value |
|---|---|---|
Stocks | 40% | $40,000 |
Bonds | 40% | $40,000 |
Commodities | 20% | $20,000 |
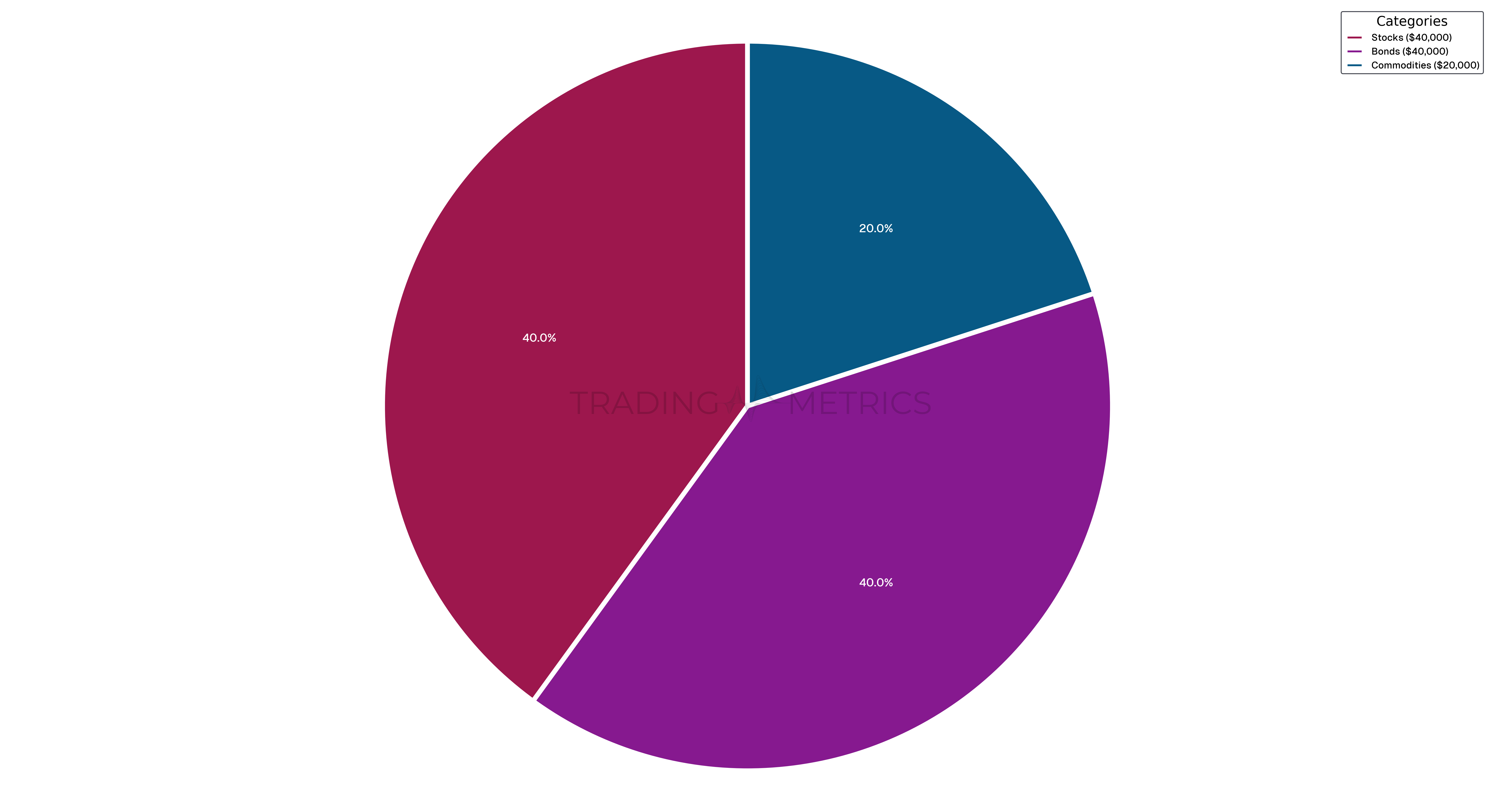
Analysis: This balanced approach helps mitigate risk by spreading investments across different asset classes. Stocks provide growth potential, bonds offer stability, and commodities can hedge against inflation. Over a period of one year, assuming an average return of 8% for stocks, 4% for bonds, and 6% for commodities, the portfolio would grow as follows:
-
Stocks: $40,000 * 1.08 = $43,200
-
Bonds: $40,000 * 1.04 = $41,600
-
Commodities: $20,000 * 1.06 = $21,200
Total portfolio value after one year: $43,200 + $41,600 + $21,200 = $106,000
Aggressive Asset Allocation
An aggressive asset allocation strategy involves a higher proportion of investments in high-risk, high-reward asset classes like stocks. Suppose a trader allocates their $100,000 portfolio as follows:
| Asset Class | Allocation | Value |
|---|---|---|
Stocks | 70% | $70,000 |
Bonds | 20% | $20,000 |
Cryptocurrencies | 10% | $10,000 |
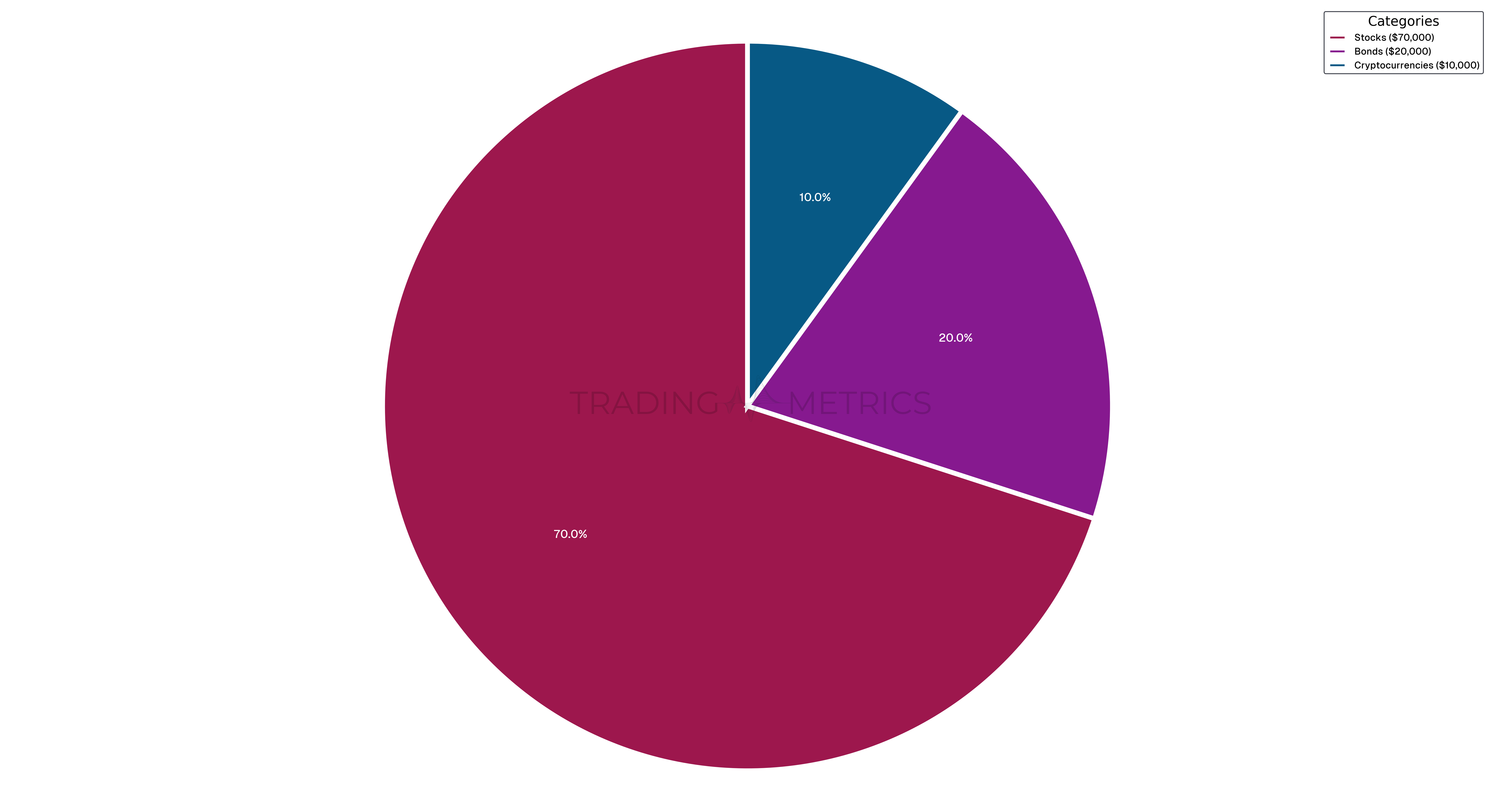
Analysis: This aggressive approach is aimed at maximizing returns, albeit with increased risk. If the stocks return 10%, bonds 3%, and cryptocurrencies 15% over a year, the portfolio performance would be:
-
Stocks: $70,000 * 1.10 = $77,000
-
Bonds: $20,000 * 1.03 = $20,600
-
Cryptocurrencies: $10,000 * 1.15 = $11,500
Total portfolio value after one year: $77,000 + $20,600 + $11,500 = $109,100
Conservative Asset Allocation
A conservative asset allocation strategy prioritizes capital preservation by investing more heavily in lower-risk asset classes. For instance, a trader might allocate their $100,000 portfolio as follows:
| Asset Class | Allocation | Value |
|---|---|---|
Stocks | 30% | $30,000 |
Bonds | 50% | $50,000 |
Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) | 20% | $20,000 |
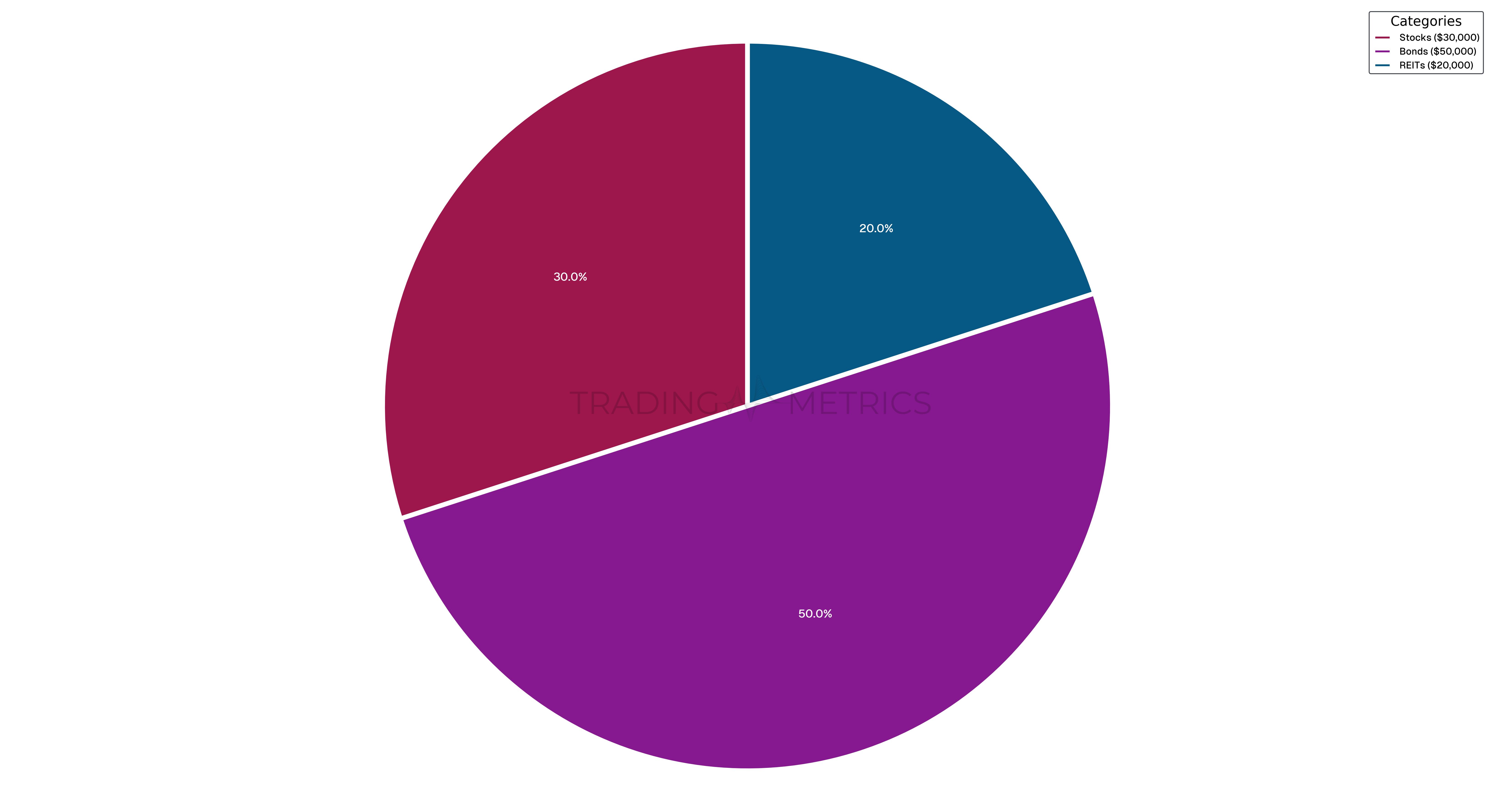
Analysis: This conservative strategy aims to reduce volatility and protect the portfolio during market downturns. Assuming stocks return 5%, bonds 3%, and REITs 4% over a year, the portfolio performance would be:
-
Stocks: $30,000 * 1.05 = $31,500
-
Bonds: $50,000 * 1.03 = $51,500
-
REITs: $20,000 * 1.04 = $20,800
Total portfolio value after one year: $31,500 + $51,500 + $20,800 = $103,800
Comparative Analysis: By comparing the outcomes of these three strategies, traders can see the impact of different asset allocations on their portfolio performance. The aggressive strategy offers the highest potential returns but comes with increased risk. The balanced strategy provides a middle ground with moderate risk and return, while the conservative strategy focuses on stability and capital preservation.
Strategy: Tailor asset allocation to your trading style. Day traders might prefer liquidity, while swing traders may lean toward higher time-frame setups.
Combining Asset Allocation with Other Tools
- Rebalancing: Regularly adjusting the portfolio to maintain the desired allocation. For instance, if Bitcoin’s value increases and it now represents 70% of Alex’s portfolio, he might sell some Bitcoin to buy more stablecoins or cash, bringing the allocation back to the original plan.
- Risk Assessment Tools: Using tools like Value at Risk (VaR) to measure and manage the risk of the portfolio.
- Technical Analysis: Combining asset allocation with technical analysis to decide the best times to enter or exit positions within each asset class.
Perspective: Factor in macroeconomic trends when allocating assets. Inflation, interest rates, and global events can impact asset performance.
Key Points
- Core Investment Strategy: Asset allocation divides investments among asset classes (e.g., stocks, bonds, real estate, cash) to achieve diversification and align with financial goals.
- Risk Management: A well-balanced allocation reduces overall portfolio risk by spreading exposure across uncorrelated asset classes.
- Customized to Goals: Tailor asset allocation based on investment objectives, time horizon, and risk tolerance, ensuring a personalized strategy.
- Dynamic Adjustments: Regularly reassess and adjust allocation to adapt to changing market conditions, life events, or financial goals.
- Impact of Market Cycles: Different asset classes perform differently in various market conditions; understanding these dynamics helps optimize allocation.
- Rebalancing for Stability: Periodic rebalancing restores the desired asset mix, maintaining the portfolio’s risk-return profile and preventing drift.
- Long-Term Growth: Higher allocations to equities may drive growth, while fixed income and cash provide stability and income in a portfolio.
- Diversification Benefits: Combining assets with varying risk levels and returns enhances portfolio resilience against market volatility.
- Geographic and Sector Allocation: Diversifying within asset classes by geography or sector further reduces concentrated risk.
- Performance Benchmarking: Compare asset allocation performance to benchmarks to evaluate effectiveness and identify areas for improvement.
Conclusion
Asset allocation is a foundational strategy in trading and investing, providing a balanced approach to risk and reward. By spreading investments across various asset classes, traders can protect against significant losses while taking advantage of diverse market opportunities. By applying these principles, you can develop a resilient and adaptable investment portfolio that aligns with your financial goals.